Before cloud
Let's say you have started a startup, and are focusing on building the platform. So, these are some of the things you have taken into consideration to make it success.
1. Backup system
2. Servers
3. Database
4. Network
5. Version control
So, you need a dedicated safe room and some computers to do all this stuff. So you build your own infrastructure (on-premise).
Problem with on-premise are:
- Server cost
- Energy cost
- Wastage of manpower (You have to have a dedicated team to focus on this)
- Work force
- Os cost
- Backup maintenance
- Scaling up and down
- Everytime when we build a new business app, we end up buying a new physical server.
So maintaining this data centres is not an easy task.
Here comes the picture of cloud computing
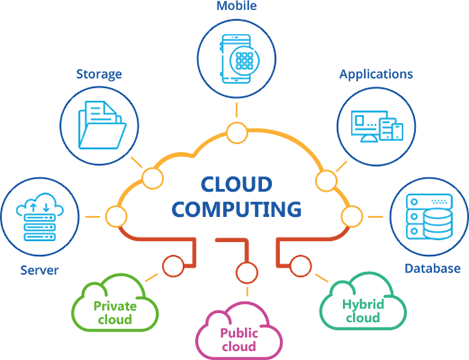
What is a Cloud?
The cloud refers to servers that are accessed over the Internet, and the software and databases that run on those servers. Cloud servers are located in data centers all over the world.
Cloud computing is the on-demand delivery of IT resources over the internet with pay-as-you-go( if you use less pay less,if you use more pay more) pricing.
Instead of buying, owning, maintaining the physical data centres and servers, you can access technology services, such as computing power, storage, and databases, on an as-needed basis from a cloud provider and just focus on building apps.
Currently AWS, Microsoft Azure, GCP are tier1 cloud providers.
Benefits of cloud computing :
Reduce cost
- Cloud reduces both capex and opex
- Organizations no longer have to spend huge amounts of money on physical servers and so on…
Pay as you go
- You'll pay for what you use.
Scalability
- Scale up, scale down, never run out of resources.
Accessibility
- Accessed from virtually anywhere at any time on any machine
Business continuity
- Any crisis do not result in data loss
Automatic updates
Increased collaboration
Self service
Some of the risk are:
- Loss of cloud data and services
- Data security
- Compliance and legal risks
- Cost concerns
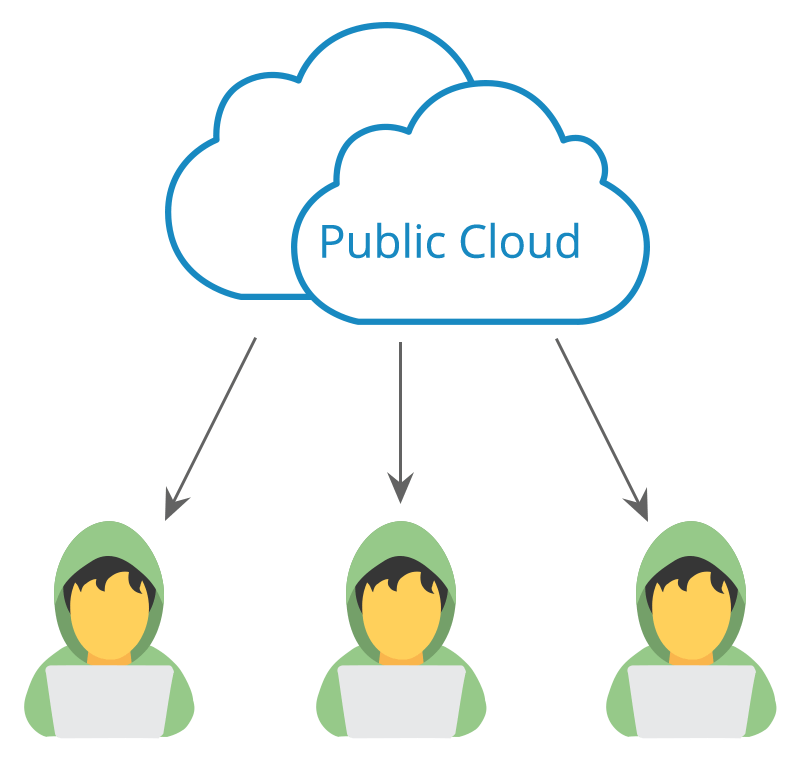
Public Cloud
Public Cloud provides a shared platform that is accessible to the general public through an Internet connection.
Physical server, storage, networking etc.., are procured and owned by the service providers. So, no setup and maintenance worries. Anyone can use public Cloud, individuals or organisations.
- Manage the cloud services and resources using cloud provider web portal
- Multi-tenancy: Multiple organisations share cloud resources
- Pay as you go
Benefits:
- No upfront capex, pay as you go
- No maintenance
- High scalable
- High reliable
- Backup and disaster recovery solutions
Limitations:
- Low visibility and control compliance and legal risks cost concerns.
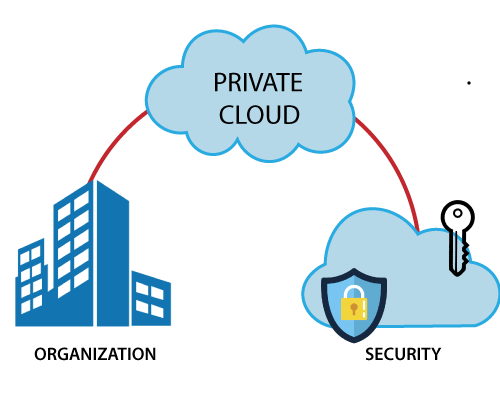
Private Cloud
Located on-premise or can be hosted by a third party service provider. Private to a specific organization. Easy to customize a private cloud . Used by government and financial agencies.
Benefits:
- Better security and control
- Legal compliance
- High regulated business
Limitations:
- Limited scalability
- Huge initial capex
- Limited access
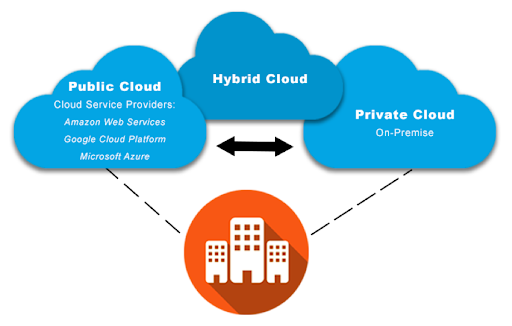
Hybrid cloud:
Private Cloud + Public Cloud
Benefits:
- Better control
- Cost effective
- App continue to run in your own private cloud.
- Burst through the public Cloud.
Limitations:
- Low visibility and control
- Additional complexity
- Compliance and legal risks
- Cost concerns
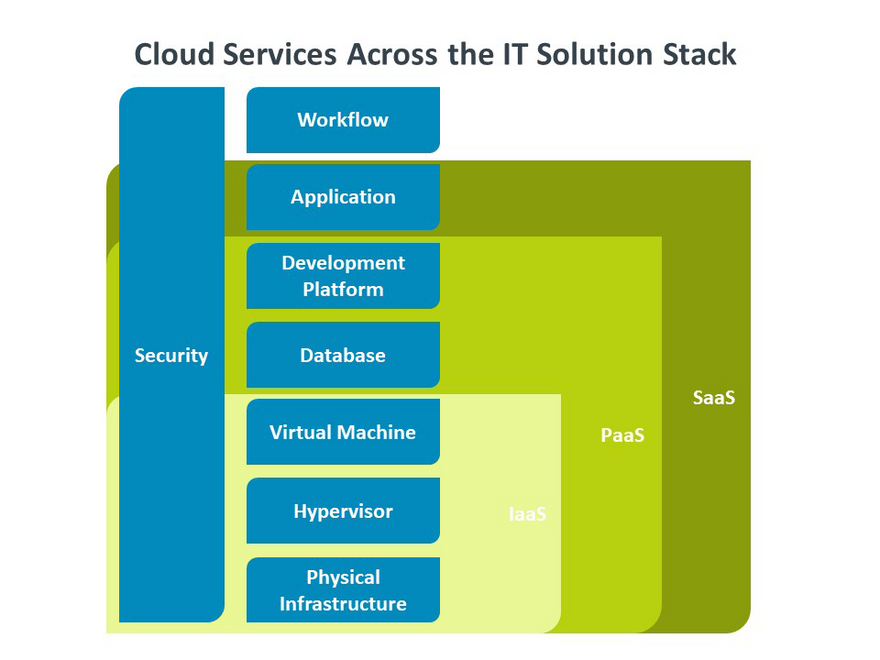
Types of cloud computing
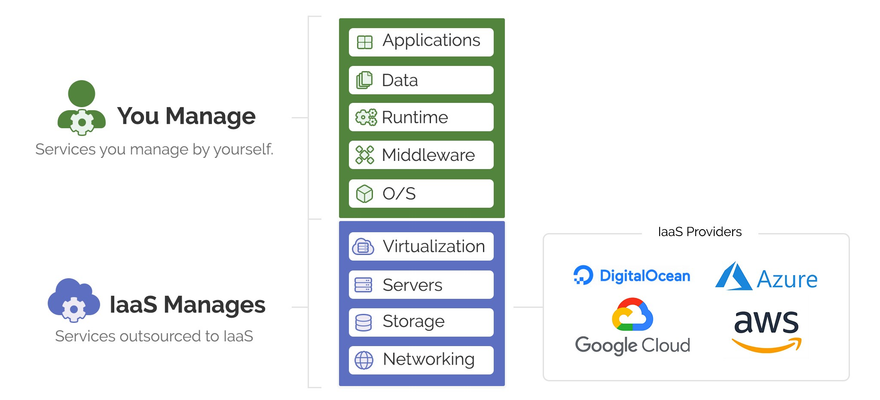
Infrastructure as a service (IaaS)
Benefits:
- Reduce financial risk
- Deployment speed
- Geographical advantages
- Unlimited scalability
Examples of IaaS are:
- AWS- Amazon Web Services
- Microsoft Azure
- Google Cloud
- Digital Ocean
- Alibaba Cloud
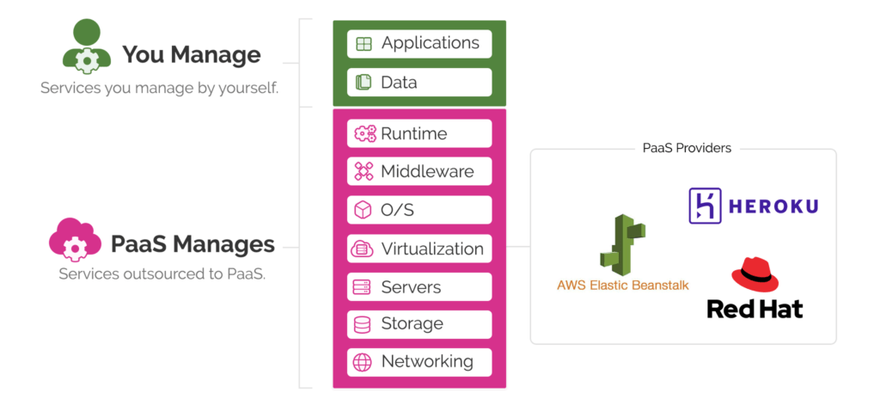
Platform as a service (Paas)
Benefits:
- Reduce development time
- Support global team
- Develop for multiplatforms
- Affordability
Examples of PaaS are:
- Heroku
- Elastic Beanstalk from AWS
- Engine Yard
- Open Shift from RedHat
Software as a service (SaaS)
Benefits:
- Very easy to get started with
- Accessibility
- Automatic updates
- Flexible usage-based pricing
- Reduce financial risks
- Affordability
Examples of Saas are:
- Netflix
- Prime
- Gmail
- Dropbox


Top comments (0)