Apractical, (relatively) easy-to-do tutorial for developing an event-driven, distributed food delivery app, just like “Uber Eats” or “Wolt”.
Many thanks to Dhanush Kamath for the use case and supporting article.
Meet Fastmart — The fastest and most reliable food delivery app ever built.
The technology stack we will use -
- Node.js as our primary dev-lang
- MongoDB for order persistency
- Memphis is a message broker for developers
- Kubernetes will host our microservices
High-Level Plan
- Install Minikube using brew package manager.
- Install Memphis over Minikube.
- Clone “Fastmart” GitHub repo.
- Review the code, the different services, and how they interact with each other.
- Deploy “Fastmart” over Kubernetes.
- Order food!
Let’s start!
1.Install Minikube
For the installation commands, please head here: https://minikube.sigs.k8s.io/docs/start/
minikube is local Kubernetes, focusing on making it easy to learn and develop for Kubernetes.
All you need is Docker (or similarly compatible) container or a Virtual Machine environment, and Kubernetes is a single command away: minikube start
What you’ll need
- 2 CPUs or more
- 2GB of free memory
- 20GB of free disk space
- Internet connection
Container or virtual machine manager, such as Docker, Hyperkit, Hyper-V, KVM, Parallels, Podman, VirtualBox, or VMware Fusion/Workstation
Output -
Verify minikube is health —
kubectl get ns
Output —
NAME STATUS AGE
default Active 31h
kube-node-lease Active 31h
kube-public Active 31h
kube-system Active 31h
2.Install Memphis
helm repo add memphis https://k8s.memphis.dev/charts/ && helm install memphis memphis/memphis — set connectionToken=”memphis” — create-namespace — namespace memphis
Let’s wait a minute or two, allowing the different components to reach “Running” state.
kubectl get pods -n memphis
Output -
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
k8s-busybox-68867bb9b7-sqdql 0/1 CrashLoopBackOff 4 (68s ago) 3m13s
memphis-broker-0 3/3 Running 4 (55s ago) 3m13s
memphis-ui-fd54f5bd6-zzqd4 0/1 CrashLoopBackOff 4 (79s ago) 3m13s
mongodb-replica-0 1/1 Running 0 3m13s
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
k8s-busybox-68867bb9b7-sqdql 0/1 CrashLoopBackOff 4 (76s ago) 3m21s
memphis-broker-0 3/3 Running 4 (63s ago) 3m21s
memphis-ui-fd54f5bd6-zzqd4 1/1 Running 5 (87s ago) 3m21s
mongodb-replica-0 1/1 Running 0 3m21s
k8s-busybox can be ignored. It will be fixed in the coming versions
3.Clone the Fastmart repo
git clone https://github.com/yanivbh1/FastMart.git
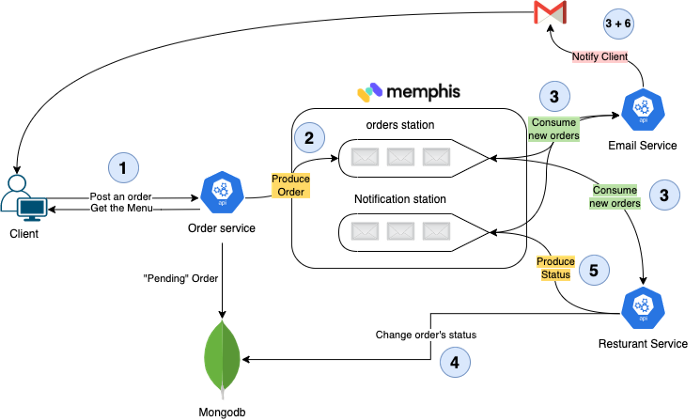
4.System Architecture, Code, and Flow
Follow the numbers to understand the flow.
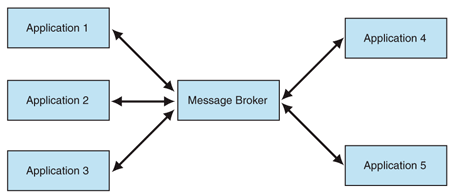
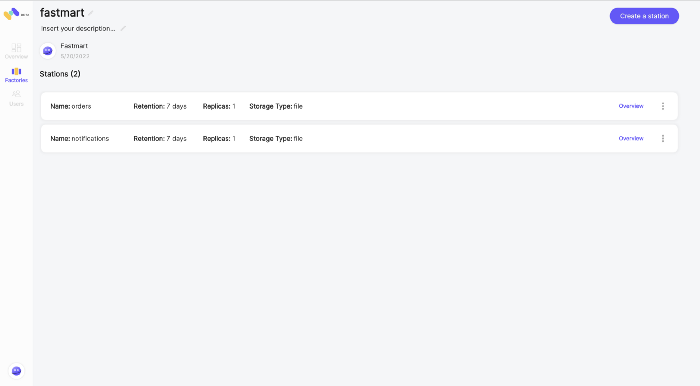
FastMart has three main components:
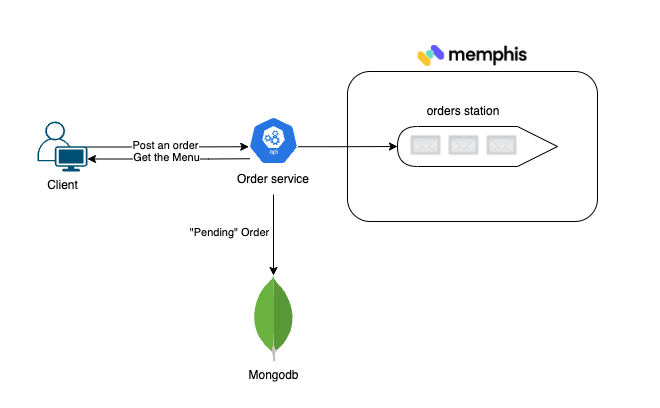
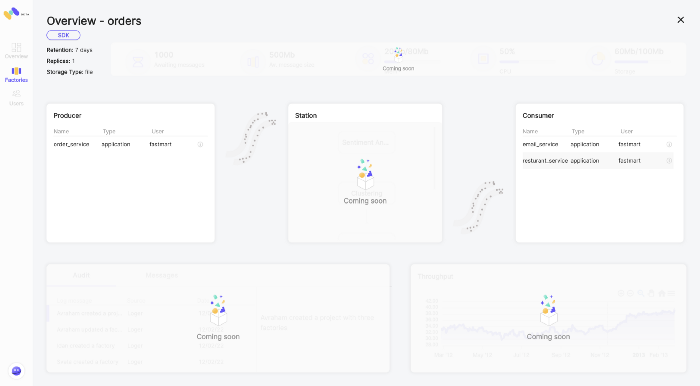
order-service - Exposes REST endpoints that allow clients to fetch the food menu, place an order and track the order in real-time.
A new order will be saved in mongo with the status “Pending” and will be produced (Pushed) into the “orders” station
GET: /<orderId>
Example: curl http://order-service:3000/30
POST: /<order_details>
Example: curl -X POST http://order-service:3000/api/orders -d ‘{“items”:[{“name”:”burger”,”quantity”:1}], “email”:”yaniv@memphis.dev”}’ -H ‘Content-Type: application/json’
The code responsible for communicating with Memphis will be found on -
./order-service/src/services/mqService.js
const memphis = require(“memphis-dev”);Memphis — trying to connect
const { logger } = require(‘./loggerService’)
const MEMPHIS_HOST = process.env.MEMPHIS_HOST || ‘localhost’; // create MQ connection string using environment variable
const MEMPHIS_USERNAME = process.env.MEMPHIS_USERNAME;
const MEMPHIS_TOKEN = process.env.MEMPHIS_TOKEN;
let ordersStation_producer = null;
const memphisConnect = async () => {
try {
logger.info()Memphis — connection established
await memphis.connect({
host: MEMPHIS_HOST,
username: MEMPHIS_USERNAME,
connectionToken: MEMPHIS_TOKEN
});
logger.info()ordersStation_producer created
ordersStation_producer = await memphis.producer({
stationName: “orders”,
producerName: “order_service”,
});
logger.info()Memphis — ${ex}`);
} catch(ex) {
logger.log(‘fatal’,
memphis.close();
process.exit();
}
}
/**
- Publish order to station
- @param {Object} order — order object containing order details
/
const publishOrderToStation = (order) => {
ordersStation_producer.produce({message: Buffer.from(JSON.stringify(order))});
logger.info(
Memphis — order ${order._id} placed); } /* - An express middleware for injecting queue services into the request object.
- @param {Object} req — express request object.
- @param {Object} res — express response object.
- @param {Function} next — express next() function. */ const injectPublishService = (req, res, next) => { // add all exchange operations here const stationServices = { publishOrderToStation: publishOrderToStation } // inject exchangeServices in request object req.stationServices = stationServices; next(); } module.exports = { injectPublishService: injectPublishService, memphisConnect: memphisConnect, }`
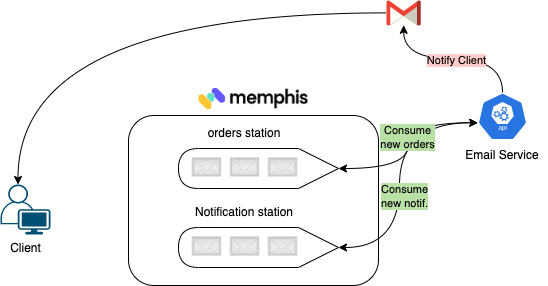
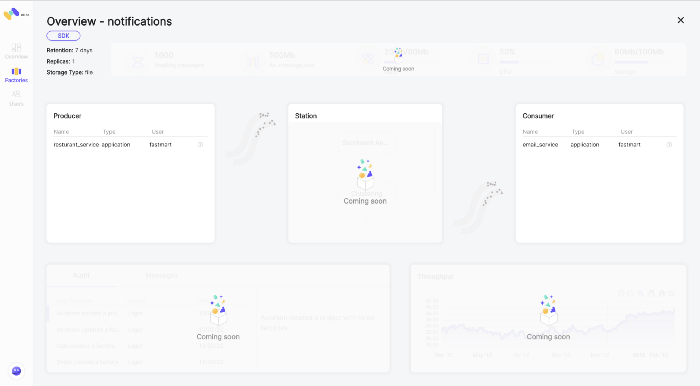
email-service - Responsible for notifying the client of the different stages.
email-service consumer messages from two stations: orders and notifications.
As soon as an order is inserted into the station, the email service notifies the client with an order confirmation.
At the same time listens for new notification requests of other services
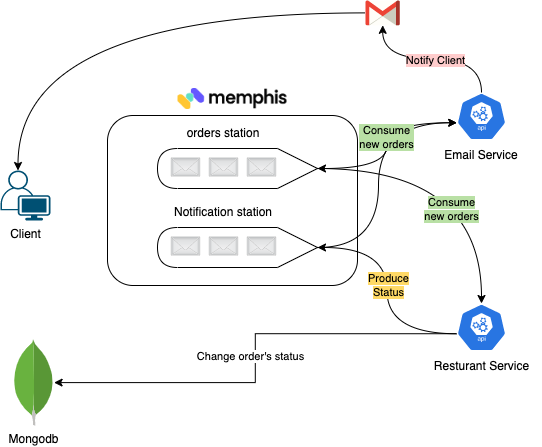
resturant-service - Responsible for fulfilling an order.
- Consume an order
- Process the order
- Change order status at the MongoDB level to “Accepted”
- Using constant sleep time to mimic the preparation of the food by the restaurant
- Change order status at the MongoDB level to “Delivered”
- Sending notification to the client
5.Deploy “Fastmart” over Kubernetes
Fastmart repo tree -
To deploy Fastmart namespace and different services,
please run kubectl apply -f k8s-deployment.yaml
kubectl get pods -n fastmart
Output -
READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
email-service-5ddb9b58d6-bq2xd 0/1 CrashLoopBackOff 3 103s
fastmart-ui-5c9bc497bd-kn4lk 1/1 Running 0 11m
orders-service-5b689b66-4h8t9 0/1 CrashLoopBackOff 7 11m
resturant-service-6d97cf6fdc-c9mvs 0/1 Completed 4 103s
Let’s understand why Fastmart services cant start
kubectl logs email-service-5ddb9b58d6-bq2xd -n fastmart
Output -
> email-service@1.0.0 start
> node ./index.js
17-05-2022 07:10:09 PM - info: Sleeping for 300ms before connecting to Memphis.
17-05-2022 07:10:09 PM - info: Memphis - trying to connect
17-05-2022 07:10:09 PM - info: email-service started
17-05-2022 07:10:09 PM - fatal: Memphis - User is not exist
It appears that the services try to connect to “Memphis” with the user “fastmart” which does not exist and we require to create it.
The simplest way to add a new user would be through the UI, but let’s do it via CLI.
Please install Memphis CLI via here.
$ mem
Usage: index <command> [options]
Options:
-V, — version output the version number
-h, — help display help for command
Commands:
connect Connection to Memphis
factory Factories usage commands
station Stations usage commands
user Users usage commands
producer Producers usage commands
consumer Consumer usage commands
init Creates an example project for working with Memphis
help display help for command
Factory is the place to bind stations that have some close business logic
Factory Commands:
ls List of factories
create Create new factory
edit Edit factory name and/or description
del Delete a factory
Station is Memphis’ queue/topic/channel/subject
Station Commands:
ls List of stations
create Create new station
info Specific station’s info
del Delete a station
Manage users and permissions
User Commands:
ls List of users
add Add new user
del Delete user
Producer is the entity who can send messages into stations
Producer Commands:
ls List of Producers
Consumer is the entity who can consume messages from stations
Consumer Commands:
ls List of Consumers
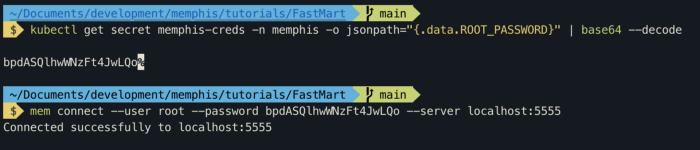
To connect the CLI with Memphis control plane we need —
- root password
kubectl get secret memphis-creds -n memphis -o jsonpath=”{.data.ROOT_PASSWORD}” | base64 — decode
OqEO9AbncKFF93r9Qd5V
- memphis control-plane url
kubectl port-forward service/memphis-cluster 7766:7766 6666:6666 5555:5555 — namespace memphis > /dev/null &
Now, connect the CLI
mem connect — user root — password bpdASQlhwWNzFt4JwLQo — server localhost:5555
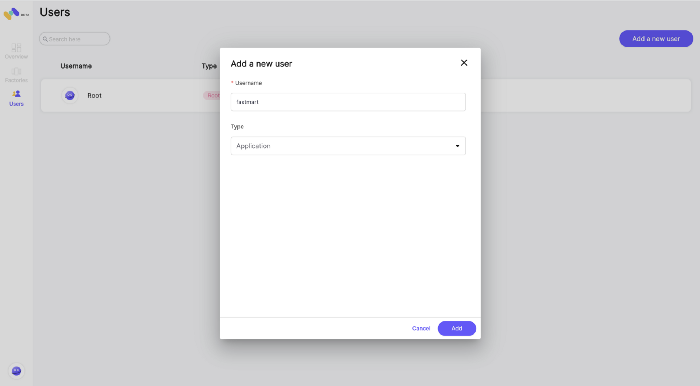
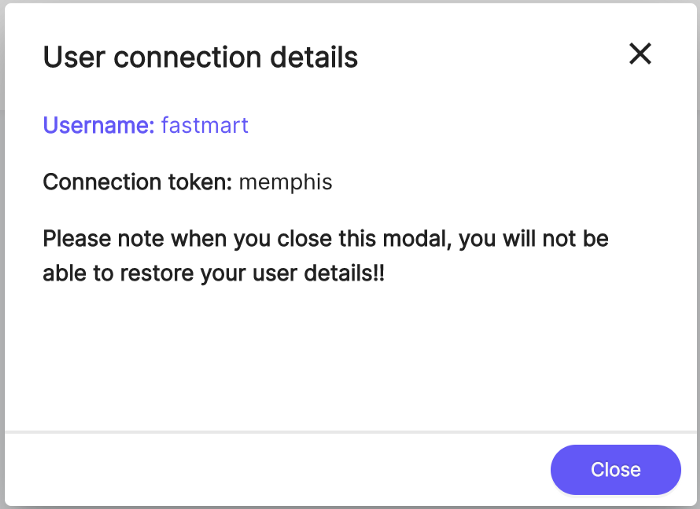
Add the user “fastmart”
mem user add -u fastmart — type application
Or via the UI
**Soon after we will create the user,
the pods will restart automatically and reconnect with Memphis.**
6.Order food!
To expose the orders-service through localhost, run -
kubectl port-forward service/orders 9001:80 — namespace fastmart > /dev/null &
Get the menu
curl localhost:9001/api/menu
Output -
{“items”:[{“name”:”burger”,”price”:50},{“name”:”fries”,”price”:20},{“name”:”coke”,”price”:10}]}
Make an order
curl -X POST localhost:9001/api/orders -d ‘{“items”:[{“name”:”burger”,”quantity”:1}], “email”:”test@gmail.com”}’ -H ‘Content-Type: application/json’
An email should arrive shortly at the email address specified above.
Thanks!




Top comments (96)
Thank you for this great post—it helped me a lot with my article. Take some time to enjoy healthy food and explore new places. Fresh air and good meals always inspire better writing.
The online portal is super easy to navigate—just enter your ticket details and you're good to go. No more waiting in line at the courthouse or stressing about missed deadlines. It’s a reliable and efficient service for anyone dealing with minor violations. Proceed to pay your ticket
Thank you for this excellent post—it was a huge support for my article. Don’t forget to care for yourself too: eat healthy food, visit new places, and recharge your mind. A fresh and energized mindset always improves your writing, so stay well and keep your creativity alive.
For those preferring not to pay online, payments can also be made by mail or in person at the respective municipal court, offering flexibility to individuals based on their preferences. Visit Now
This article serves as a detailed guide to building a food delivery app like DoorDash. It covers the use of technologies such as Node.js, MongoDB, and Kubernetes, providing step-by-step instructions for development. The guide highlights the importance of an event-driven architecture and a message broker for seamless operation. With insights into system design, deployment, and testing, it’s a valuable resource for developers aiming to create a dependable food delivery platform. Click Here
“This is a great guide for developers interested in building delivery apps like DoorDash. If you’re more into exploring food and drink options instead, you can check Caffe Nero hot chocolate price and explore their full menu.”
The best part is, once you complete the survey, you usually get a validation code for a free sandwich or discount offer on your next visit! The step-by-step instructions on MyBKExperienceSurvey.us are really helpful, especially if you’re not sure how to find the right codes on your receipt. my bk experience mybkexperience.com get your survey rewards
Building a food delivery app like DoorDash can be enhanced with an event-driven architecture using technologies such as Node.js and MongoDB, just like Fastmart. Integrating message brokers like Memphis ensures real-time updates, similar to the way Chipotlemenuus manages its online orders. By using Kubernetes to host services, you can scale and manage multiple microservices effortlessly, optimizing both speed and reliability.
Every day is a good day for Popeyes! Explore today’s menu to find new flavors, limited-time specials, and classic meals that always satisfy. poppeyesmenu.com/
Skip the line and enjoy your meal from home! Order Ambers online for quick pickup or delivery, and enjoy your favorite fried chicken without the wait. ambermenu.com.ph/
The ALDI ad this week starts Wednesday, bringing fresh deals on groceries, produce, and limited-time ALDI Finds. Shop midweek to catch the best savings before they're gone!
This is an awesome hands-on tutorial for building a scalable food delivery app like DoorDash using modern tools like Kubernetes, Node.js, and Memphis. If you're exploring real-world food delivery concepts, you should also check out Menu for delicious menu inspiration while you build.
In a world full of cluttered websites and shallow advice, mynstromy.com feels like a breath of fresh air. The topics are relevant, the design is clean, and the tips they provide are practical and easy to follow. A solid resource for anyone trying to level up my nord strom: access portal online - mynordstrom.com
Some comments may only be visible to logged-in visitors. Sign in to view all comments.